Submitting tender bids has typically involved a substantial amount of manual work, but with the emergence of AI, traditional processes have begun to change. Among other notable advancements, AI can now automatically summarise procurement documents. But beyond a convenience factor, what are the actual benefits of automatic summaries?
In this article, we explore the risks of manual processes and the benefits of automatic summaries.
What is a Manual Summary?
First, let’s define what we’re talking about. What do manual processes used by so many bid teams today look like?
Deciding whether to proceed with a bid is often a complex decision, one that involves considering several parameters. Bid teams often must verify and approve information, requirements, and contract terms, and in handling such decisions internally, many opt to create manual summaries.
The process begins once a relevant procurement opportunity has been found. This most often requires teams to enter procurement tools, review tender notices, and download related documents. Thereafter, bidding teams set themselves to review the documents, and any requirements and additional information contained in these. In some instances, teams will upload documents to a shared space, to avoid each team member needing to retrieve or store the documentation.
The next step in the process is to create the manual summary, which serves as an initial introduction and basis for discussion. The summary is used by teams to better prepare them in making a decision on whether or not to proceed with a bid. here some might use advanced Excel sheets, others may keep extensive checklists in order to keep track of the information.
The process is repeated over and over again for each tender notice and opportunity that at first glance seems viable. For companies dealing with an extensive number of public procurement opportunities, the process might take place several times a day, and ultimately, is a time-consuming task for most bidding teams.
So, what are some of the consequences to consider when working with manual summaries?
1. Missing Vital Information
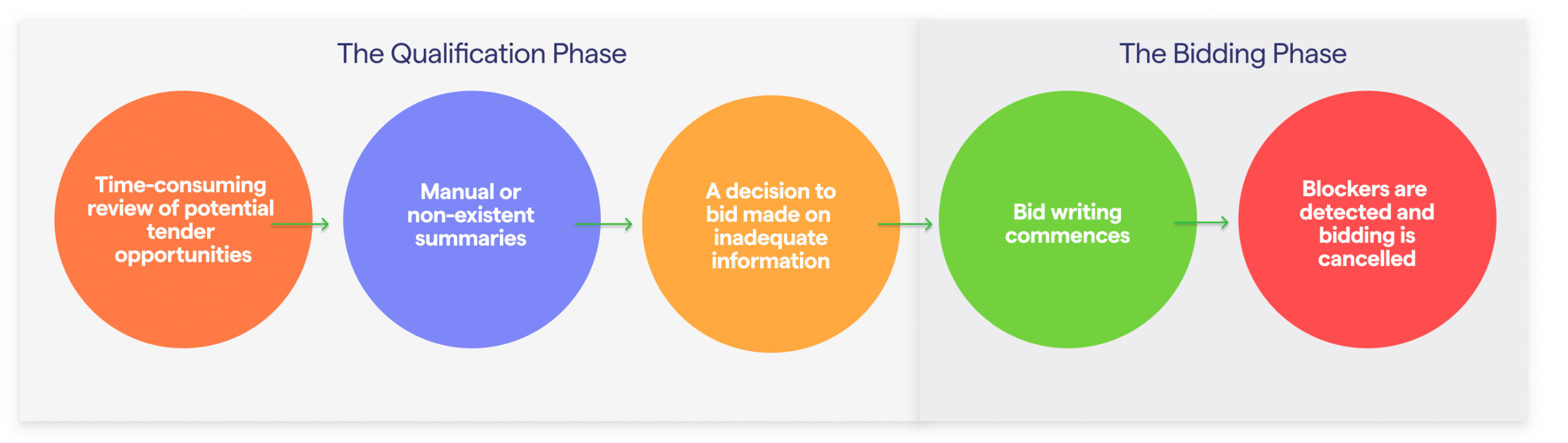
As the process is continuously repeated, and several procurement opportunities might need to be summarised in a short period of time, important information can easily be lost by the wayside. It is not uncommon that a manual summary might have missed crucial information or a key requirement, matters so important that they could come to change the final decision. After all, to err is human, and mistakes are made. Manual processes also lead to an increased error rate, especially when compared to automated processes.
Essential information that might be overlooked can include both requirements and conditions outlined in the tender documents. Or it might rather be a case of simply making poor judgements – judgements made based on inadequate information. But more on this shortly.
2. Managing Information Inefficiently
Many companies don’t create any type of summary at all, finding it easiest to skip the summarization step altogether. However, the process remains manual and often sees a bid manager review documents to evaluate whether the tender is a relevant business opportunity or not. A bid manager might then proceed by forwarding the entire tender documentation to, say, their sales manager for further review.
Is this efficient? A sales manager will often have several other priorities, but equally, knows that significant contracts can be crucial. They might quickly skim through the documents, and might perhaps not be well-versed in legal jargon, unsure where to find the truly relevant information. Cautious not to miss a potential win, they inform the bid manager that the opportunity looks promising, and the bid manager gets to work.
Just as with manual summaries, the lack of a summary means decisions to proceed are often made on insufficient and inadequate information. This brings us to the next risk.
3. Decisions Based on Assumptions
Both manual summaries and the absence of summaries altogether lead to the same central problem. Decisions to proceed to the bid writing stage are based on inadequate information and sometimes outright incorrect assumptions.
Incorrect decision-making often leads to severe and costly consequences. Preparing a formal bid takes a lot of time, involves senior personnel or stakeholders, and could incur significant costs for a company should it ultimately be a wasted effort. Bidding teams never want to begin preparing a bid, only to realise a few days later that a crucial requirement isn’t met, a legal condition can’t be accepted, or a reference requirement hasn’t been examined thoroughly.
Ultimately, bidding processes like these lead to an inefficient use of resources, and an unnecessarily low number of successful bids, the consequences of which can be rather disastrous.
4. Excessive Time Spent in the Qualification Phase/in Qualifying Procurements
Nonetheless, a seasoned bidding team will still be fully able to make good decisions on which tenders to proceed with, and the previous risk might thus not be the most common scenario. But another aspect to consider is, how much time does a bidding team spend reaching these decisions?
Overall, an organization often invests a lot of time in qualifying and reviewing procurement opportunities. Most understand the consequences of making poor decisions and know that it might be wise to spend more time in the initial qualification phase, to avoid spending time on unviable opportunities later on. So, checklists and spreadsheets are used to ensure all vital requirements and conditions are reviewed, and bidding teams manually compile this information to avoid committing each point to memory. Once the bidding team’s qualification is complete, a compiled list is sent to relevant stakeholders who in turn review the information and provide their perspectives. Only then can a final decision to proceed be made.
Since deadlines can be demanding, and as there are only 30 days to submit a bid on average, the number of days spent on qualifying a tender opportunity can be crucial. Should the qualification phase be a lengthy process, significant time that could be spent elsewhere is consumed. Long lead times and time-consuming compilations lead to inefficiencies. It is safe to say that both bidding teams and organisations strive to make well-informed decisions as quickly as possible, to have the most amount of time to put together the best possible and most competitively advantageous bid.
5. Poor Use of Resources
Time-consuming and error-ridden manual processes contribute to inefficiencies and time lost. As irrelevant or unviable procurements slip through, and wasted time is spent, less time remains for teams to produce competitive bids for viable opportunities. In the long run, they also mean that bidding teams allocate a higher degree of resources per each successful bid they submit.
The net result is a team that, despite having the capacity to win more, ends up stuck in unnecessarily manual processes involving unviable and irrelevant tender opportunities.
A bidding process with manual summaries might look like this:
How Do Automatic Summaries Benefit the Bidding Process?
Now that we’ve discussed the consequences of engaging in manual summary processes during the qualification phase, what’s the alternative? How do automatic summaries affect and optimise the tendering process?
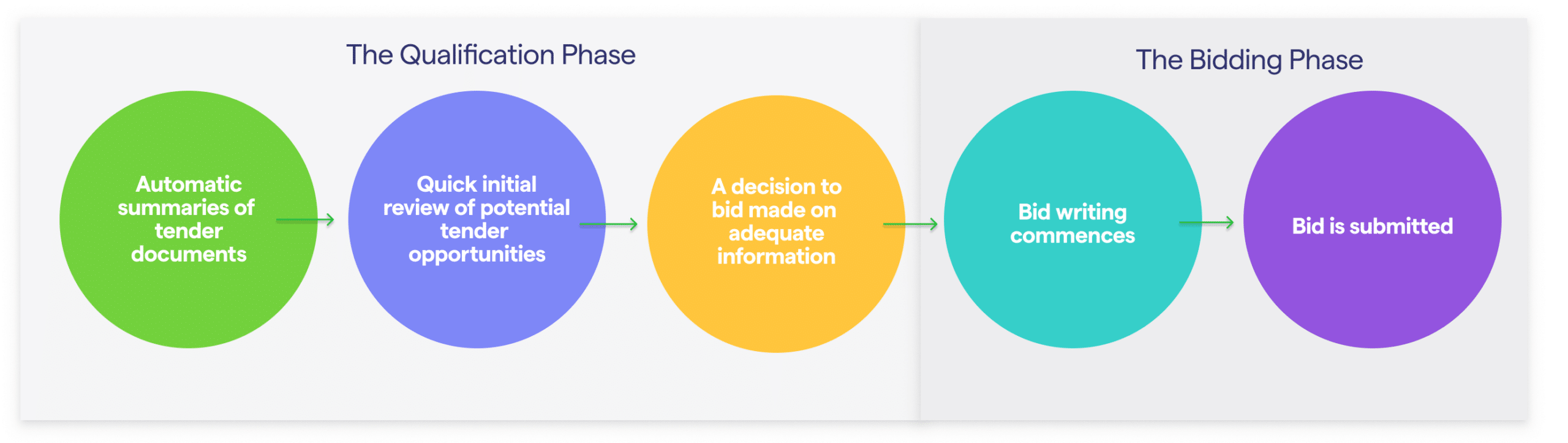
What we at Tendium consider automatic summaries are AI-generated compilations of essential information and requirements which are gathered from relevant procurement documents – presented on the Tendium platform. The summary can also be customised to include any specific requirements or conditions that are critical to your business and bidding process, and that are make-or-break in determining if opportunities are viable. You can determine these points beforehand, and adjust the conditions and requirements you wish to locate whenever a new one might become relevant to you.
Our automatic summaries are instrumental in both the initial assessment and qualification phase and during decision-making meetings. No longer do bid managers need to spend time creating checklists, committing vast amounts of information to memory, or compiling manual summaries.
The results are noticeable throughout the entire bidding process.
- A standardized and less person-dependent process. The entire team is provided with a summary to rely on. Should the responsible bid manager be sick or otherwise unavailable, no matter, the summary is still there.
- Avoid spending time compiling information manually. Bid managers can review documentation and identify risks or technical blockers far faster and with a reduced error rate. The risk of missing crucial and critical information is thus reduced.
- Decisions earlier on in the bidding process. Automatic summaries can be provided to all stakeholders with only a few clicks, allowing your organisation to come together and discuss, saving precious time and resources. Far more than what would be possible if relying on traditional manual processes.
- Reduced number of time-consuming decision meetings, or perhaps no decision meetings at all. With a centralized space for everyone in an organisation to evaluate bids and collaborate, it is far easier to make decisions on the go. No more recurring weekly decision meetings – phew!
A Bidding process with automatic summaries might instead look like this:
The Positive Effects are Evident
The effects of bidding processes that include automatic summaries are clear.
- Fewer bids abandoned, and therefore more attention is spent towards opportunities one stands a chance of winning.
- Significant time savings and lower costs, as fewer irrelevant procurements slip through and human errors are reduced.
- Increasing chances to win contracts, and improving the accuracy of viable bids submitted.
Leveraging automatic summaries, teams can spend time on genuinely relevant procurements, better bids can be written, and more time can be dedicated to analyzing prices and the competitive context for each potential contract. Decisions are also better grounded with automatic summaries, allowing more time towards putting together competitive bids.
We at Tendium are pleased that automatic summaries can contribute to a better, smoother and more efficient bidding process. While manual processes have dominated the market, and time-consuming and costly processes have been the norm, things are changing!